Dairy-CropSyst

Installation package
This is "in-house" development version of the coupled Dairy and CropSyst model, with a simple user interface and example project.Manual
Description
Dairy confined animal feeding operations (CAFOs) may have deleterious effects on the environment by concentrating nutrients and emitting high amounts of greenhouse gasses (GHG). To reduce these effects in the United States, CAFOs are required to implement plans to minimize the natural resource contamination and to report GHG and ammonia emissions that exceed EPA guidelines.The IPCC protocol for GHG emission lack the farm level resolution, similarly the use of constant emission factors has proven insufficient for quantifying the gaseous emission from livestock operations. Use of modelling tool may aid in planning and evaluating farm scale mitigation efforts. A model that accommodate the impact of existing and emerging manure treatments on emissions and nutrient fate would provide more comprehensive simulation for a whole-farm nutrients budget.
Dairy-CropSyst is a decision support tool for CAFOs managers and researchers to evaluate the effects of manure treatment options on net GHG emissions and manure nutrients fate applied to crop land. Dairy-CropSyst tracks the nutrients and gaseous emissions from dairy CAFO through multiple modular components (Figure 1). This is accomplished by integrating established models dealing with manure production and associated emission on during manure management, performance parameters of different manure treatments from industry data and literature, and using the cropping systems model CropSyst.
Inputs for the dairy module include daily weather and unit operation specific parameters. A fertigation schedule may be defined if a field is to be simulated. Field parameters include weather, soil, and crop management. The model outputs a detailed daily of nutrient production, transformation, volatilization, leaching, flow between component facilities and residual soil nutrient balance in soil. Outputs are summarized in an Excel workbook.
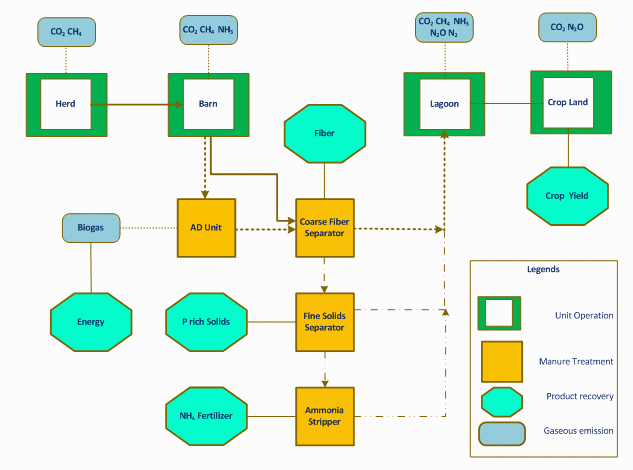
Modeling and analysis:
Tariq M. Khalil
Claudio O. Stöckle
Nicole Uslar-Valle
Craig S. Frear
Data and support:
Jingwei Ma
Stewart S. Higgins
April B. Leytem
Robert S. Dungan
Programming and design: